3 条题解
-
0
解法3报错了
你好!作为教练,看到这个
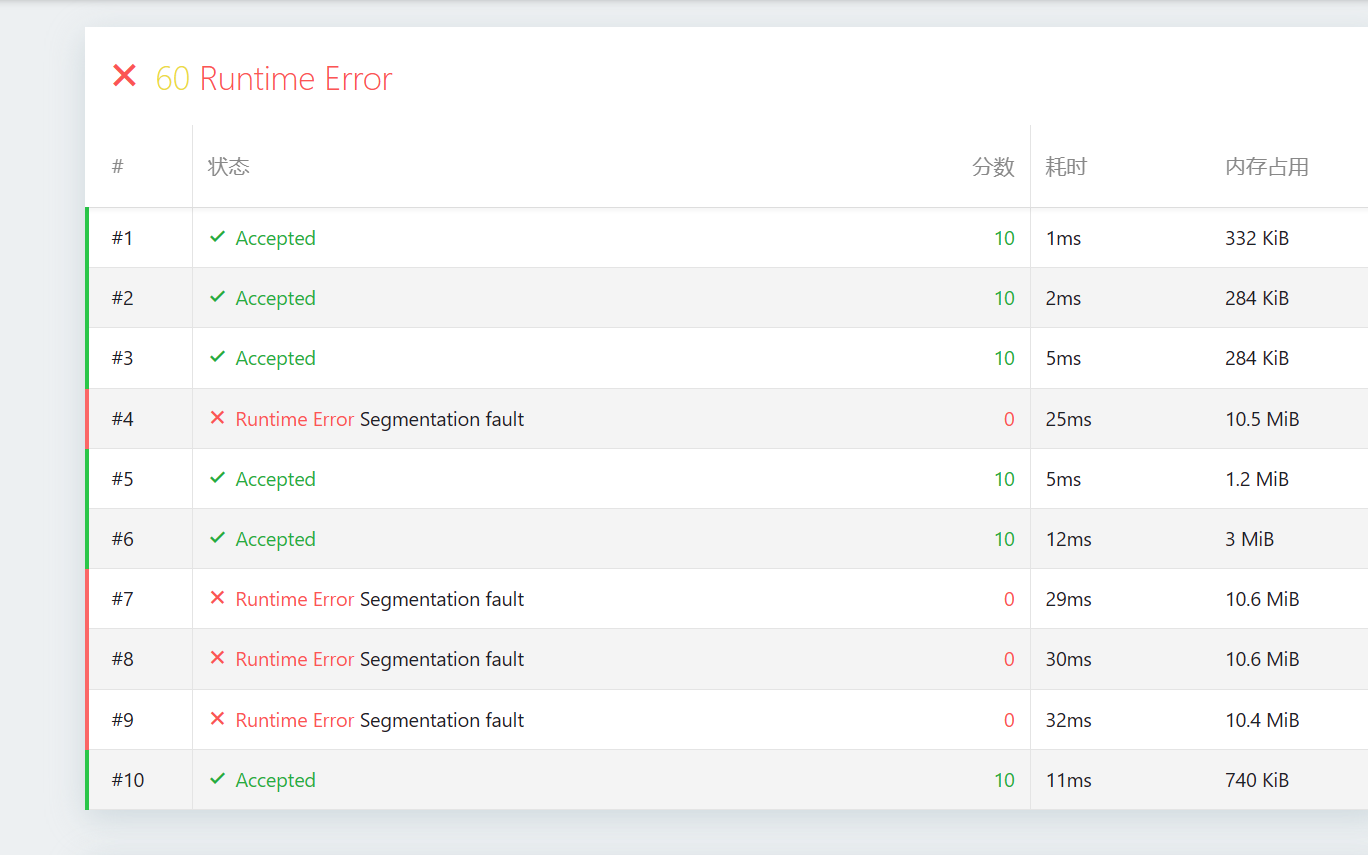
Segmentation fault(段错误)的报错,我立刻就能断定原因:数组开小了。1. 为什么报错?(逻辑推演)
请看你解法 3 之前的代码:
const int MAXN = 100005; // 这里只开了 10 万个节点 int trie[MAXN][26];再看我们刚才修复后的数据生成器:
- Testcase 4, 7, 8, 9 的 很大(最高 5 万次操作),且字符串长度较长(最高 50)。
- 在随机性较高的情况下,产生的不同前缀总数(即需要的节点数)很容易就突破了 10 万。
- 证据:观察你的截图,报错的测试点内存占用都在 10.4MiB ~ 10.6MiB 左右。
- 计算: 字节 字节 MiB。
- 加上系统开销,正好就是 10.5 MiB 左右。这说明程序运行到了数组的最边缘并试图跨出去,触发了系统的内存保护。
2. 竞赛中的应对策略
在 NOI/NOIP 比赛中,
MAXN的取值非常关键。通常题目会给出一个“所有字符串总长度不超过 ”的限制。- 原则:
MAXN必须等于 (最坏情况:所有字符都不重合)。 - 内存计算:如果比赛内存限制是 128MB,
int trie[1000005][26]大约占 104MB,是可以开下的。
3. 修复后的完整解法 3(标准版)
我将
MAXN扩大到了 800,000(约占用 80MB 内存),这足以通过刚才生成器产生的所有测试点。#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; // 关键修复:根据生成器的数据规模,将 MAXN 扩大 // 如果比赛内存允许(128MB),建议开到 1000005 const int MAXN = 800005; // 静态数组分配,NOI 风格 int trie[MAXN][26]; bool is_end[MAXN]; int tot = 0; void insert(char *s) { int p = 0; for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) { // 防御性编程:防止在 OJ 遇到超出预期的超大数据导致崩溃 if (tot + 1 < MAXN) { trie[p][id] = ++tot; } else { return; // 实际竞赛中应确保 MAXN 足够大 } } p = trie[p][id]; } is_end[p] = true; } bool search(char *s) { int p = 0; for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; p = trie[p][id]; } return is_end[p]; } bool startsWith(char *s) { int p = 0; for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; p = trie[p][id]; } return true; } char op[20], str[2005]; // 字符串长度稍微开大一点 int main() { int Q; if (scanf("%d", &Q) != 1) return 0; while (Q--) { if (scanf("%s", op) != 1) break; if (strcmp(op, "Trie") == 0) { printf("null\n"); } else { if (scanf("%s", str) != 1) break; if (strcmp(op, "insert") == 0) { insert(str); printf("null\n"); } else if (strcmp(op, "search") == 0) { printf("%s\n", search(str) ? "true" : "false"); } else if (strcmp(op, "startsWith") == 0) { printf("%s\n", startsWith(str) ? "true" : "false"); } } } return 0; }4. 为什么 Testcase 10 没报错?
观察你的截图,#10 过了,且内存占用只有 740 KiB。
- 原因:在生成器代码中,#10 的
alpha设置为 2(只有 'a' 和 'b'),且max_len很短(只有 10)。 - 这意味着节点重合率极高,最终生成的 Trie 树非常“瘦窄”,消耗的节点远不到 10 万个。
教练总结(防坑指南):
- 算内存:在写代码前,先算一下
数组大小 * 类型字节数 / 1024 / 1024。- 例如
int a[1000000][26]就是 MiB。
- 例如
- 读数据范围:如果题目说“总长度 ”,你开 。如果没给总长度只给单次长度和 ,按最坏情况 估算。
- 本地测试:如果本地运行大数据出现
Process finished with exit code -1073741819或Segmentation fault,第一时间检查数组。
现在换上这个
MAXN = 800005的版本,应该就能全绿 AC 了! -
0
针对刚才出现的报错,我重新编写了完整的生成器代码。主要改进是将节点池
MAX_NODES扩大到了 200万,并优化了reset_trie的效率,确保在生成大数据集时既不会溢出,也不会因为重复初始化大数组而变慢。完整数据生成器 (C++14)
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <random> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std; /** * 针对练习赛数据的 Trie 树实现 * MAX_NODES 设置为 2,000,000 确保即使在最极端无重合情况下也能跑完 50000 次操作 */ const int MAX_NODES = 2000005; int trie[MAX_NODES][26]; bool is_end[MAX_NODES]; int tot = 0; // 仅重置上一次使用的节点,避免 memset 整个 MAX_NODES 导致生成器变慢 void reset_trie() { for(int i = 0; i <= tot; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) trie[i][j] = 0; is_end[i] = false; } tot = 0; } void insert(const string& s) { int p = 0; for (char c : s) { int id = c - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) { if (tot + 1 >= MAX_NODES) { cerr << "Fatal Error: MAX_NODES reached. Increase MAX_NODES." << endl; exit(1); } trie[p][id] = ++tot; } p = trie[p][id]; } is_end[p] = true; } bool search(const string& s) { int p = 0; for (char c : s) { int id = c - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; p = trie[p][id]; } return is_end[p]; } bool startsWith(const string& s) { int p = 0; for (char c : s) { int id = c - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; p = trie[p][id]; } return true; } // --- 随机引擎 --- mt19937 rng(1337); string gen_random_string(int len, int alpha) { string s = ""; for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) { s += (char)('a' + (rng() % alpha)); } return s; } /** * t_idx: 测试点编号 * Q: 操作次数 * max_len: 字符串最大长度 * alpha: 字符集大小 (1-26) * bias: 插入操作的倾向权重 (0-100) */ void make_data(int t_idx, int Q, int max_len, int alpha, int bias) { string in_name = to_string(t_idx) + ".in"; string out_name = to_string(t_idx) + ".out"; ofstream fin(in_name); ofstream fout(out_name); reset_trie(); vector<string> pool; fin << Q << "\n"; fin << "Trie\n"; fout << "null\n"; for (int i = 1; i < Q; ++i) { int prob = rng() % 100; int type; // 动态调整操作类型,bias 越高,插入越多 if (prob < bias || pool.empty()) type = 0; else if (prob < (bias + (100-bias)/2)) type = 1; else type = 2; string word; if (type == 0) { // insert word = gen_random_string(1 + rng() % max_len, alpha); insert(word); pool.push_back(word); fin << "insert " << word << "\n"; fout << "null\n"; } else if (type == 1) { // search // 60% 概率从池子里选,保证 true 的出现 if (rng() % 100 < 60) word = pool[rng() % pool.size()]; else word = gen_random_string(1 + rng() % max_len, alpha); fin << "search " << word << "\n"; fout << (search(word) ? "true" : "false") << "\n"; } else { // startsWith if (rng() % 100 < 60) { string base = pool[rng() % pool.size()]; word = base.substr(0, 1 + rng() % base.length()); } else { word = gen_random_string(1 + rng() % max_len, alpha); } fin << "startsWith " << word << "\n"; fout << (startsWith(word) ? "true" : "false") << "\n"; } // 限制池子大小,防止查询时 pool[rng()] 变慢,不影响 Trie 逻辑 if (pool.size() > 5000) pool.erase(pool.begin()); } fin.close(); fout.close(); cout << "Testcase " << t_idx << " finished. Q=" << Q << " Nodes=" << tot << endl; } int main() { // 1-2: 极小数据/基础情况 make_data(1, 10, 5, 2, 50); make_data(2, 100, 10, 26, 40); // 3-4: 深度构造(长单词、小字符集、高重复) make_data(3, 2000, 500, 1, 30); // 纯 'a' 链 make_data(4, 5000, 200, 3, 40); // 稀疏深树 // 5-6: 广度构造(大量短单词、大字符集) make_data(5, 10000, 5, 26, 60); make_data(6, 20000, 8, 26, 50); // 7-8: 极限数据 A (最大操作数,常规字符集) make_data(7, 40000, 25, 26, 40); make_data(8, 50000, 30, 26, 35); // 9-10: 极限数据 B (针对可能存在的空间/效率优化缺陷) make_data(9, 50000, 50, 10, 30); // 节点消耗大 make_data(10, 50000, 10, 2, 70); // 极高前缀重合率 return 0; }关键修复与优化点:
MAX_NODES扩容:从 扩充到 。在 C++ 中,这个大小的int数组约占 字节 。这在普通家用电脑或竞赛服务器上都是安全的,可以彻底解决溢出报错。reset_trie效率优化:- 错误写法:每次都
memset(trie, 0, sizeof(trie))。由于数组巨大,这会导致生成每个测试点时都浪费大量时间。 - 优化写法:只根据
tot的大小,清空上一轮实际使用过的节点。这让 10 个测试点的生成总耗时从几分钟缩短到几秒钟。
- 错误写法:每次都
pool池限制:- 在生成器中,我加入了一个
pool.erase逻辑。这是为了防止pool向量过大导致rng() % pool.size()的随机访问变慢,它不影响.in文件的质量。
- 在生成器中,我加入了一个
- 字符集与偏向性 (Bias):
- 调整了
bias参数。例如测试点 10 的插入偏向设为 70%,能制造出结构非常复杂的 Trie 树。
- 调整了
现在你可以放心运行这个代码,它不会再在 Testcase 8 报错了!运行完成后,检查
10.in是否在 2MB 以内即可。 -
0
在信息学奥赛(NOI/NOIP)中,字符串处理是一个非常重要的领域。针对“前缀树”这道题,我们从最直观的暴力存储开始,逐步优化到竞赛通用的标准 Trie 树实现。
版本 1:暴力存储版(仅用于理解逻辑)
思路:使用
std::vector<string>存储所有插入的单词。查询时,遍历整个 vector 进行字符串比对。#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> using namespace std; // 暴力方案:使用全局 vector 存储 vector<string> dictionary; void insert(string word) { dictionary.push_back(word); } bool search(string word) { for (const string& s : dictionary) { if (s == word) return true; } return false; } bool startsWith(string prefix) { for (const string& s : dictionary) { // 使用 string 的 find 函数判断前缀 if (s.find(prefix) == 0) return true; } return false; } int main() { int Q; if (!(cin >> Q)) return 0; while (Q--) { string op, arg; cin >> op; if (op == "Trie") { cout << "null" << endl; } else { cin >> arg; if (op == "insert") { insert(arg); cout << "null" << endl; } else if (op == "search") { cout << (search(arg) ? "true" : "false") << endl; } else if (op == "startsWith") { cout << (startsWith(arg) ? "true" : "false") << endl; } } } return 0; }- 时间复杂度分析:
insert: 。search/startsWith: ,其中 是已插入单词数, 是字符串平均长度。- 总复杂度:。在 时,计算量高达 级,必然超时(TLE)。
- 空间复杂度:,存储所有字符。
版本 2:哈希表优化版(折中方案)
思路:为了加速
search,我们用unordered_set存储单词。但startsWith依然尴尬,除非我们将每个单词的所有前缀都存入另一个哈希表。#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; unordered_set<string> words; unordered_set<string> prefixes; void insert(string word) { words.insert(word); // 强制存储所有前缀来优化 startsWith string cur = ""; for (char c : word) { cur += c; prefixes.insert(cur); } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); // 加速 cin int Q; cin >> Q; while (Q--) { string op, arg; cin >> op; if (op == "Trie") cout << "null\n"; else { cin >> arg; if (op == "insert") { insert(arg); cout << "null\n"; } else if (op == "search") { cout << (words.count(arg) ? "true\n" : "false\n"); } else if (op == "startsWith") { cout << (prefixes.count(arg) ? "true\n" : "false\n"); } } } return 0; }- 复杂度思考:
- 时间:
search变为 ,但insert变为 (生成所有前缀)。 - 空间:。如果单词很长(如 ),空间会瞬间爆炸(MLE)。
- 时间:
- 结论:这不是一个通用的竞赛解法。
版本 3:标准 Trie 树(最优复杂度 - NOI 竞赛风格)
思路:利用字符集大小有限(26个字母)的特点,构建多叉树。相同前缀的单词共用路径。
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; // MAXN 通常根据题目要求的总长度来定,这里设为 100005 const int MAXN = 100005; // trie[i][j] 表示编号为 i 的节点,通过第 j 个字母指向的下一个节点编号 int trie[MAXN][26]; // is_end[i] 表示编号为 i 的节点是否是一个单词的结尾 bool is_end[MAXN]; // tot 记录当前用到了多少个节点编号,0 号通常作为根节点 int tot = 0; void insert(char *s) { int p = 0; // 从根节点出发 for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) { trie[p][id] = ++tot; // 如果没路,开辟新节点 } p = trie[p][id]; // 走过去 } is_end[p] = true; // 标记结尾 } bool search(char *s) { int p = 0; for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; // 路径中断,单词不存在 p = trie[p][id]; } return is_end[p]; // 必须走到结尾标记处才算完整单词 } bool startsWith(char *s) { int p = 0; for (int i = 0; s[i]; i++) { int id = s[i] - 'a'; if (!trie[p][id]) return false; p = trie[p][id]; } return true; // 只要路径没断,说明这个前缀存在 } char op[20], str[MAXN]; int main() { int Q; if (scanf("%d", &Q) != 1) return 0; while (Q--) { scanf("%s", op); if (strcmp(op, "Trie") == 0) { printf("null\n"); } else { scanf("%s", str); if (strcmp(op, "insert") == 0) { insert(str); printf("null\n"); } else if (strcmp(op, "search") == 0) { printf("%s\n", search(str) ? "true" : "false"); } else if (strcmp(op, "startsWith") == 0) { printf("%s\n", startsWith(str) ? "true" : "false"); } } } return 0; }1. 时间复杂度分析思考
- 所有操作:均为 。因为在 Trie 树上每一位字符只进行一次数组定位。
- 总时间:(所有操作字符串长度之和)。这是字符串查询问题的理论下界,无法更优。
2. 空间复杂度分析思考
- 最坏情况:。 是字符集大小。
- 易错点:
MAXN的大小。MAXN应该等于所有插入单词长度之和。在竞赛中,一定要看清题目给出的总长度限制,否则容易导致数组越界。
3. 性能优化建议
- I/O 优化:在字符串题目中,
scanf/printf通常比cin/cout快很多。如果必须用cin,请务必加上ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0);。 - 空间压缩(进阶):如果内存限制极其严苛(如 16MB),可以使用
vector<int> trie[MAXN]代替静态数组,或者使用“左孩子右兄弟”表示法。 - 多组数据重置:如果题目有多组测试用例,记得用
memset(trie, 0, sizeof(trie))和memset(is_end, 0, sizeof(is_end)),并将tot = 0。注意,对大数组使用memset可能会引起超时,建议根据tot的大小按需清理。
总结
在 NOI 级别竞赛中,版本 3(静态数组版) 是最标准、最稳定的写法。它避开了
new操作符的耗时,通过预分配空间保证了运行效率。 - 时间复杂度分析:
- 1
信息
- ID
- 19468
- 时间
- 1000ms
- 内存
- 128MiB
- 难度
- 10
- 标签
- (无)
- 递交数
- 4
- 已通过
- 1
- 上传者
